- If inverted output of D flip-flop is connected to its input how the flip-flop behaves?
- Design a circuit to divide input frequency by 2?
- Design a divide by two counter using D-Latch.
- Design a divide-by-3 sequential circuit with 50% duty cycle.
- What are the different types of adder implementation?
- Draw a Transmission Gate-based D-Latch?
- Give the truth table for a Half Adder. Give a gate level implementation of the same.
- Design an OR gate from 2:1 MUX.
- What is the difference between a LATCH and a FLIP-FLOP?
- Design a D Flip-Flop from two latches.
- Design a 2 bit counter using D Flip-Flop.
- What are the two types of delays in any digital system
- Design a Transparent Latch using a 2:1 Mux.
- Design a 4:1 Mux using 2:1 Mux's.
- What is metastable state? How does it occur?
- What is metastablity?
- Design a 3:8 decoder
- Design a FSM to detect sequence "101" in input sequence
- Convert NAND gate into Inverter in two different ways.
- Design a D and T flip flop using 2:1 mux only.
- Design D Latch from SR flip-flop.
- Define Clock Skew, Negative Clock Skew, Positive Clock Skew?
- What is race condition? How it occurs? How to avoid it?
- Design a 4 bit Gray Counter?
- Design 4-bit synchronous counter, asynchronous counter?
- Design a 16 byte asynchronous FIFO?
- What is the difference between a EEPROM and FLASH?
- What is the difference between a NAND-based Flash and NOR-based Flash?
- Which one is good: asynchronous reset or synchronous reset? Why?
- Design a simple circuit based on combinational logic to double the output frequency.
- What is the difference between flip-flop and latch?
- Implement comparator using combinational logic, that compares two 2-bit numbers A and B. The comparator should have 3 outputs: A > B, A < a =" B.">
- Give two ways of converting a two input NAND gate to an inverter?
- What is the difference between mealy and moore state-machines?
- What is the difference between latch based design and flip-flop based design?
- What is metastability and how to prevent it?
- Design a four-input NAND gate using only two-input NAND gates.
- Why are most interrupts active low?
- How do you detect if two 8-bit signals are same?
- 7 bit ring counter's initial state is 0100010. After how many clock cycles will it return to the initial state?
- Design all the basic gates NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR using 2:1 Multiplexer.
- How will you implement a full subtractor from a full adder?
- In a 3-bit Johnson's counter what are the unused states?
- What is difference between RAM and FIFO?
- What is an LFSR? List a few of its industry applications.
- Implement the following circuits:
(a) 3 input NAND gate using minimum number of 2 input NAND gates
(b) 3 input NOR gate using minimum number of 2 input NOR gates
(c) 3 input XNOR gate using minimum number of 2 input XNOR gates assuming 3 inputs A,B,C? - Design a D-latch using (a) using 2:1 Mux (b) from S-R Latch?
- How to implement a Master Slave flip flop using a 2 to 1 mux?
- How many 2 input xor's are needed to inplement 16 input parity generator?
- Convert xor gate to buffer and inverter.
- Difference between onehot and binary encoding?
- What are different ways to synchronize between two clock domains?
- How to calculate maximum operating frequency?
- How to find out longest path?
- How to achieve 180 degree exact phase shift?
- What is significance of ras and cas in SDRAM?
- Tell some of applications of buffer?
- Implement an AND gate using mux?
- What will happen if contents of register are shifter left, right?
- What is the basic difference between analog and digital design?
- What advantages do synchronous counters have over asynchronous counters?
- What types of flip-flops can be used to implement the memory elements of a counter?
- What are the advantages of using a microprocessor to implement a counter rather than the conventional method (flip-flop and logic gates)?
- What is the principal advantage of Gray Code over straight (conventional) binary?
- What does Pipelining do?
- Design divide by 2, divide by 3 circuit with equal duty cycle.
- How many 4:1 mux do you need to design a 8:1 mux?
- What is D-Word, Q-word?
- Define Moore, Mealy state machines. Which one is good for timing?
- Design a FSM to detect 10110. What is the minimum number of flops required?
- Design a simple circuit based on combinational logic to double the output frequency.
- Design a 2bit up/down counter with clear using gates. (No verilog or vhdl)
- Design a finite state machine to give a modulo 3 counter when x=0 and modulo 4 counter when x=1.
- Minimize: S= A' + AB
- What is the function of a D-flipflop, whose inverted outputs are connected to its input?
- How to synchronize control signals and data between two different clock domains?
- Describe a finite state machine that will detect three consecutive coin tosses (of one coin) that results in heads.
- In what cases do you need to double clock a signal before presenting it to a synchronous state machine?
- How many bit combinations are there in a byte?
- What are the different Adder circuits you studied?
- Give the truth table for a Half Adder. Give a gate level implementation of the same.
- Convert 65(Hex) to Binary
- Convert a number to its two's compliment and back.
- What is the 1's and 2's complement of the decimal number 25.
- If A?B=C and C?A=B then what is the boolean operator ?
Showing posts with label Digital Design. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Digital Design. Show all posts
Saturday, January 15, 2011
Digital design Interview Questions
Thursday, July 22, 2010
Digital System and Binary Numbers
Digital Systems:
I have got many emails from students regarding Digital System and Binary Numbers conecpts so this is quick review what is Digital System and Binary Numbers? and what it does.....i think it will help u guys...if u guys really intersted and want to become logical designer Download this book Digital Design (4th Edition) only book that can tech u basics in professional way recommended by many designers...
only book that can tech u basics in professional way recommended by many designers...
I have got many emails from students regarding Digital System and Binary Numbers conecpts so this is quick review what is Digital System and Binary Numbers? and what it does.....i think it will help u guys...if u guys really intersted and want to become logical designer Download this book Digital Design (4th Edition)
Digital systems are used in:
called a bit, has two values: 0 or 1.
Example: The decimal digits a through 9 are represented in digital system with a code
of four bits (e.g. is represented by 0111, 8 is represented by 1000, 9 is represented by
1001).
- Communication
- Business transaction
- Traffic Control
- Medical treatment
- Internet
called a bit, has two values: 0 or 1.
Example: The decimal digits a through 9 are represented in digital system with a code
of four bits (e.g. is represented by 0111, 8 is represented by 1000, 9 is represented by
1001).
Binary Numbers
- Decimal number:
(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9).
Example:
The decimal number 245 may be written as
2x102+4x101+5x100
where 2, 4, and 5 are the coefficients.
- Binary Number System:
Example:
(1001)2 its equivalent decimal number is : 1x23+0x22+0x21+1x20 = 8 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 9
where 1, 0, 0, and 1 are the coefficients.
where 1, 0, 0, and 1 are the coefficients.
- Octal number system (Base 8):
The octal number system is said to be of base, or radix, '8' because it uses digits
(00, 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17).
(00, 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17).
- Hexadecimal number system (Base 16):
It uses 16 digits : (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F). The letter A, B, C, D, E,
and F are used for the digits 10,11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 respectively.
Example:
(124)16 = 1x162 + 2x161 + 4x160= 256 + 32 + 4 = 292
and F are used for the digits 10,11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 respectively.
Example:
(124)16 = 1x162 + 2x161 + 4x160= 256 + 32 + 4 = 292
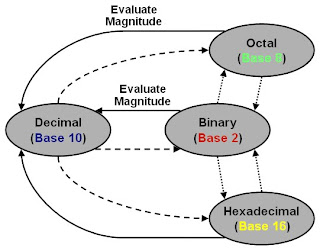
NUMBER BASE CONVERSION
Decimal to Binary conversion
- Divide the number with base '2'.
- Take the remainder 0 or 1 as a coefficient.
- Take the quotient and repeat the division.
Decimal to Octal conversion
Binary to Octal conversion
Binary to Hexadecimal
Octal to Hexadecimal conversion
Complements:
The meaning of complement is something required to make a thing complete. For example, salsa complements tortilla chips, beer complements pizza, an ice cream cone complements a hot summer day, and apple sauce complements pork chops. A key concept to explore is how two things complement each other. For example, when a piece of pizza is removed from a whole pizza the piece complements what is left behind and vice versa. Each of the 4 following complements use the same concept except in different bases and what is considered a complete number in that base.
- 1’s Complement:
- 2’s ComplementFinding the 8 digit 2’s complement of 01101100
- 9’s ComplementThe 9’s complement finds whatever is needed to make an entire set of 9’s. This is shown in the
- 10’s ComplementFinding the 5 digit 10’s complement of 1357
Basic Logic Gate
A logic gate performs a logical operation on one or more logic inputs and produces a single logic output. The logic normally performed is Boolean logic and is most commonly found in digital circuits. Logic gates are primarily implemented electronically using diodes or transistors, but can also be constructed using electromagnetic relays (relay logic), fluidic logic, pneumatic logic, optics, molecules, or even mechanical elements.In electronic logic, a logic level is represented by a voltage or current, (which depends on the type of electronic logic in use). Each logic gate requires power so that it can source and sink currents to achieve the correct output voltage. In a pure logic diagram logic levels and power supply connections do not exist and are not shown, but in a full logic circuit diagram, documenting the implementation of the logic, these are required.
All other types of Boolean logic gates (i.e., AND, OR, NOT, XOR, XNOR) can be created from a suitable network of NAND gates. Similarly all gates can be created from a network of NOR gates. Historically, NAND gates were easier to construct from MOS technology and thus NAND gates served as the first pillar of Boolean logic in electronic computation.
Truth table is a table that describes the behaviour of a logic gate or any combination of logic gates. It lists the value of the output for every possible combination of the inputs and can be used to simplify the number of logic gates and level of nesting in an electronic circuit. In general the truth table does not lead to an efficient implementation; a minimization procedure, using Karnaugh maps, the Quine–McCluskey algorithm or an heuristic algorithm is required for reducing the circuit complexity.
Truth table & Symbols
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)